Page 16 - Artha
P. 16
Domestic Trends
reduction in imports of software, travel and business CII remains optimistic about investment, and an anticipated
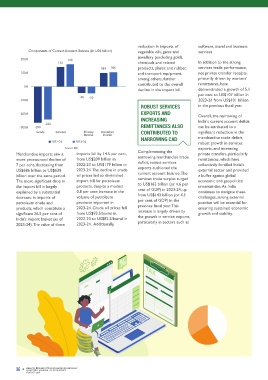
Components of Current Account Balance (in US$ billion) vegetable oils, gems and services. A Turbocharged India's economic prospects, rebound in global trade.
jewellery (excluding gold), projecting an impressive Headwinds from geopolitical
200.0 163
143 chemicals and related In addition to the strong growth rate of 8 per cent in tensions, volatility in
101 106 products, plastic and rubber, services trade performance, the current fiscal year. This international commodity
100.0 and transport equipment, net private transfer receipts, Indian Economy optimism is rooted in three prices, and geoeconomic
among others, further primarily driven by workers’ key factors: stabilization of fragmentation, however, pose
contributed to the overall remittances, have inflation, resurgence in private risks to the outlook.
0.0
decline in the import bill. demonstrated a growth of 5.1
per cent to US$107 billion in
-46 -50 Set for 8%+
-100.0 2023-24 from US$101 billion
ROBUST SERVICES in the previous fiscal year.
-200.0 EXPORTS AND Overall, the narrowing of
INCREASING India's current account deficit Growth in FY25
-242
-300.0 -265 REMITTANCES ALSO can be attributed to a
Goods Services Primary Secondary CONTRIBUTED TO significant reduction in the
Income Income
NARROWING CAD merchandise trade deficit,
2022-23 2023-24 robust growth in services
Source: RBI exports, and increasing
Merchandise imports saw a imports fell by 14.5 per cent, Complementing the private transfers, particularly
more pronounced decline of from US$209 billion in narrowing merchandise trade remittances, which have he Indian economy has next five years, as per the
7 per cent, decreasing from 2022-23 to US$179 billion in deficit, robust services collectively fortified India's T demonstrated remarkable projections of the
US$686 billion to US$638 2023-24. The decline in crude exports cushioned the external sector and provided resilience and strength, International Monetary Fund
billion over the same period. oil prices led to diminished current account balance. The a buffer against global defying prevailing global (IMF). During this period, as
The more significant drop in import bill for petroleum services trade surplus surged economic and geopolitical economic and geopolitical per CII Research projections,
the import bill is largely products, despite a modest to US$163 billion (or 4.6 per uncertainties. As India headwinds. With a India’s GDP is projected to
ndia recorded a surplus in US$1.3 billion deficit (or 0.2 explained by a substantial 0.8 per cent increase in the cent of GDP) in 2023-24, up continues to navigate these higher-than-expected real more than double from
the current account after a per cent of GDP) during the decrease in imports of volume of petroleum from US$143 billion (or 4.3 challenges, strong external GDP growth of 8.2 per cent US$3.5 trillion to US$ 8
gap of 10 quarters, marking a same quarter in the previous petroleum crude and products imported in per cent of GDP) in the position will be essential for in 2023-24, India has firmly trillion, thereby gliding to its Private consumption remains domestic demand drivers,
significant turnaround in its year. On an annual basis, the products, which constitute a 2023-24. Crude oil prices fell previous fiscal year. This ensuring sustained economic established itself as the fastest position as the third-largest strong with steady therefore, appear robust,
external dynamics. The current account deficit significant 26.5 per cent of from US$93.5/barrel in increase is largely driven by growth and stability. growing major economy in economy globally. discretionary spending in providing a strong buffer
current account posted a moderated to US$23.2 billion, India’s import basket (as of 2022-23 to US$82.3/barrel in the growth in service exports, the world for three urban areas. The one against looming challenges.
surplus of US$5.7 billion, representing 0.7 per cent of 2023-24). The value of these 2023-24. Additionally, particularly in sectors such as consecutive years. In tandem The remarkable performance year-ahead, RBI’s consumer
representing 0.6 per cent of GDP in 2023-24, a with its strong growth of the Indian economy is confidence remains in the On the external front, India’s
GDP in the fourth quarter of remarkable reduction from potential, India's stock market underpinned by robust optimistic terrain in May. resilient services export
2023-24, a stark contrast to US$66.9 billion (or 2 per cent recently crossed the US$5.0 macroeconomic fundamentals, Rural demand is also reviving growth has played a pivotal
US$8.7 billion deficit (or 0.1 of GDP) in the preceding trillion valuation, making it the thriving manufacturing and with improvement in farm role in stabilizing the
per cent of GDP) recorded in fiscal year. Annually, goods trade deficit fourth largest equity market services sector, and buoyant sector activity. Growth of economy, keeping the current
the preceding quarter and contracted from US$265 globally and giving it a place domestic demand. Further, retail two-wheeler sales, account deficit at manageable
billion (7.9 per cent of GDP) among the world’s stock the government’s strategic moderation in contraction of levels, and mitigating the
in 2022-23 to US$242 billion market superpowers. focus on investment in tractor sales and pick up in impact of global economic
(or 6.8 per cent of GDP) in infrastructure- both physical FMCG volume growth fluctuations. In 2023-24,
2023-24. & digital- while maintaining suggest a recovery in rural services exports surged by
INDIA’S ASCENDANCE fiscal prudence has fortified demand. The reduction in 4.9 per cent to US$341
The turnaround into a surplus This contraction can be AS A RISING macroeconomic growth and demand for MNREGA jobs by billion, propelled by the rapid
in Q4 of 2023-24 was majorly traced to a larger decline in ECONOMIC POWER stability. The robustness of the 14.3 per cent year-on-year in proliferation of Global
attributed to narrowing of the merchandise imports economy is evident from the May 2024 reflects an Capability Centres (GCCs) in
merchandise trade deficit. The compared to exports. high-frequency data, including improvement in regular India. Additionally, foreign
goods trade deficit Specifically, merchandise The increasing prominence of rising manufacturing and employment. Further, the direct investment (FDI)
contracted to US$50.9 billion exports fell by 3.3 per cent, Indian economy on the global services PMI, high credit prospects of an above-normal inflows have shown robust
(or 5.4 per cent of GDP) in amounting to US$439 billion stage is also reinforced by its growth, and robust GST monsoon by the Indian growth in recent years, with
Q4 of 2023-24, a notable in 2023-24, down from substantial share in global collections in the first quarter Meteorological Department India maintaining its status as
reduction from US$69.9 US$454 billion in 2022-23 GDP, which is expected to of current fiscal, confirming an (IMD) are expected to boost the leading destination for
billion (or 7.7 per cent of due to slowdown in the rise from the current 16 per improvement in industrial agricultural productivity and greenfield FDI in the
GDP) in the preceding global economy coupled with cent to 18 per cent over the activity. bolster rural demand. These Asia-Pacific region.
quarter and US$52.6 billion in geopolitical disruptions that
Q4 of the previous fiscal year. weakened external demand.
16 ANALYSIS, RESEARCH, THOUGHT LEADERSHIP & ADVOCACY ANALYSIS, RESEARCH, THOUGHT LEADERSHIP & ADVOCACY 17
QUARTERLY JOURNAL OF ECONOMICS
QUARTERLY JOURNAL OF ECONOMICS
AUGUST 2024 AUGUST 2024